GitHub Copilot Web’s Superpower: Wider context for Holistic Quality of microservices
GitHub Copilot’s Superpower: Understanding Microservices in Context — A New Era for Holistic Quality
In modern, event-driven architectures, microservices communicate through streams, messages, and shared contracts. Tools like Apache Kafka, Apache Pulsar, RabbitMQ, and NATS are foundational to this pattern. But with that comes complexity — and a major challenge:
How do you understand the impact of a change when your system is spread across 10, 20, or even 50 microservices?
Traditionally, this has been a pain point — not only for QA Automation Engineers but also for Product Engineers and Architects. Gaining visibility into cross-service dependencies often meant hours of manual tracing and unclear communication paths.
When working in a microservices ecosystem:
- A simple feature change may trigger multiple downstream events
- It’s hard to foresee the ripple effects during the Discovery phase
- Integration-level visibility is often missing or buried in documentation
This gap makes end-to-end (E2E) validation of event flows difficult — and risks go unnoticed until later stages.
That’s where GitHub Copilot Web in Agent Mode brings in a game-changing ability:
Widening the context to analyze and reason across many repositories at once.
This isn’t just about code suggestions — it’s about enabling holistic quality thinking across a distributed system, starting as early as the Discovery phase.
Why GitHub Copilot Web (Agent Mode) Is a Game Changer
One of the most powerful and underrated features of GitHub Copilot Web in Agent Mode is its ability to handle wider context — across multiple repositories at once.
In large-scale systems where services are distributed and interdependent, understanding the full picture often requires:
- Jumping between codebases
- Manually tracing event definitions and handlers
- Syncing with multiple teams
Copilot Web Agent removes that friction. It can:
- Read through many repositories simultaneously
- Understand shared event contracts and communication patterns
- Generate contextual outputs like diagrams, summaries, or even visual workflows
This unlocks entirely new ways to support impact analysis, architecture visualization, and automated documentation — especially during the Discovery phase of development.
Use Case: AI-Generated Event Flow Diagrams Between Microservices
In a recent experiment, I used Copilot Web (Agent Mode) to help visualize how events flowed between several microservices.
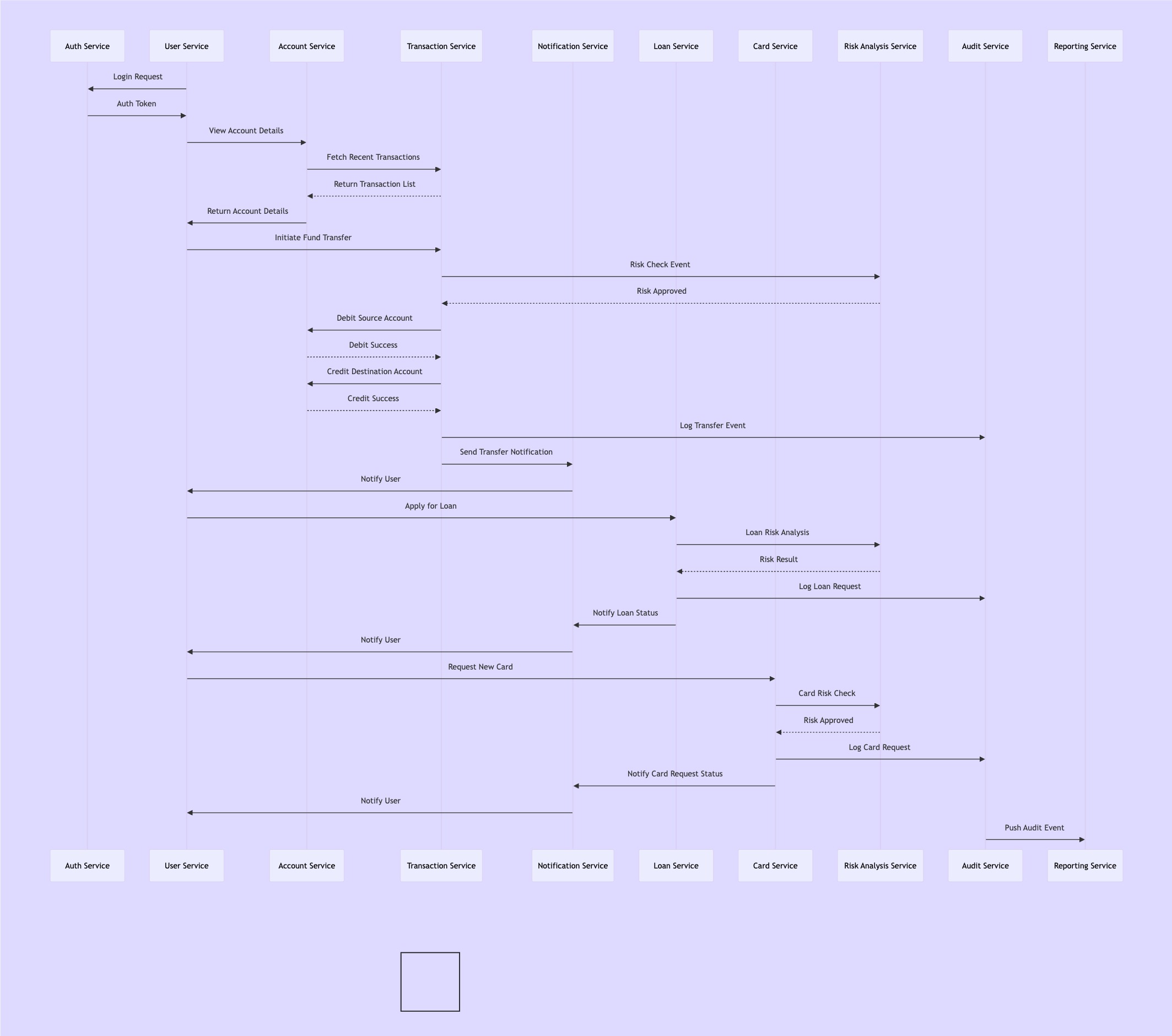
Objective:
Generate a Mermaid diagram that maps out all events exchanged among microservices in the system.
My Prompt:
“Select the attached services under ‘Parent repo’ as the context. As a QA engineer, I want to create an impact chart of any change introducing to any service, and event messaging between micro-services. As an expert solution architect, can you create a mermaid syntax of all the events happening between micro-services? Mention the exact names of events in the connection lines/arrows, and provide steps to create a graphical dependency diagram. Also, create a Miro board using the Mermaid diagram.”
What Copilot Did:
- Parsed multiple services in the provided repo group
- Identified the relevant event publishers and consumers
- Generated a valid Mermaid syntax graph
- Provided clear steps to render the diagram visually using Miro or similar tools
This drastically improved visibility for both Product and QA teams — before any implementation began.
Why This Matters
- Product teams can foresee side effects before development begins
- Engineers gain confidence in their change impact
- QA teams can test smarter, not harder
- Discovery becomes collaborative and data-driven
So,
What used to be a black box between microservices can now be mapped and understood — with the help of AI.
This makes Discovery more powerful, actionable, and collaborative than ever before.
The life of engineers is becoming easier, and smarter.
Let’s start designing systems with visibility, right from the start.